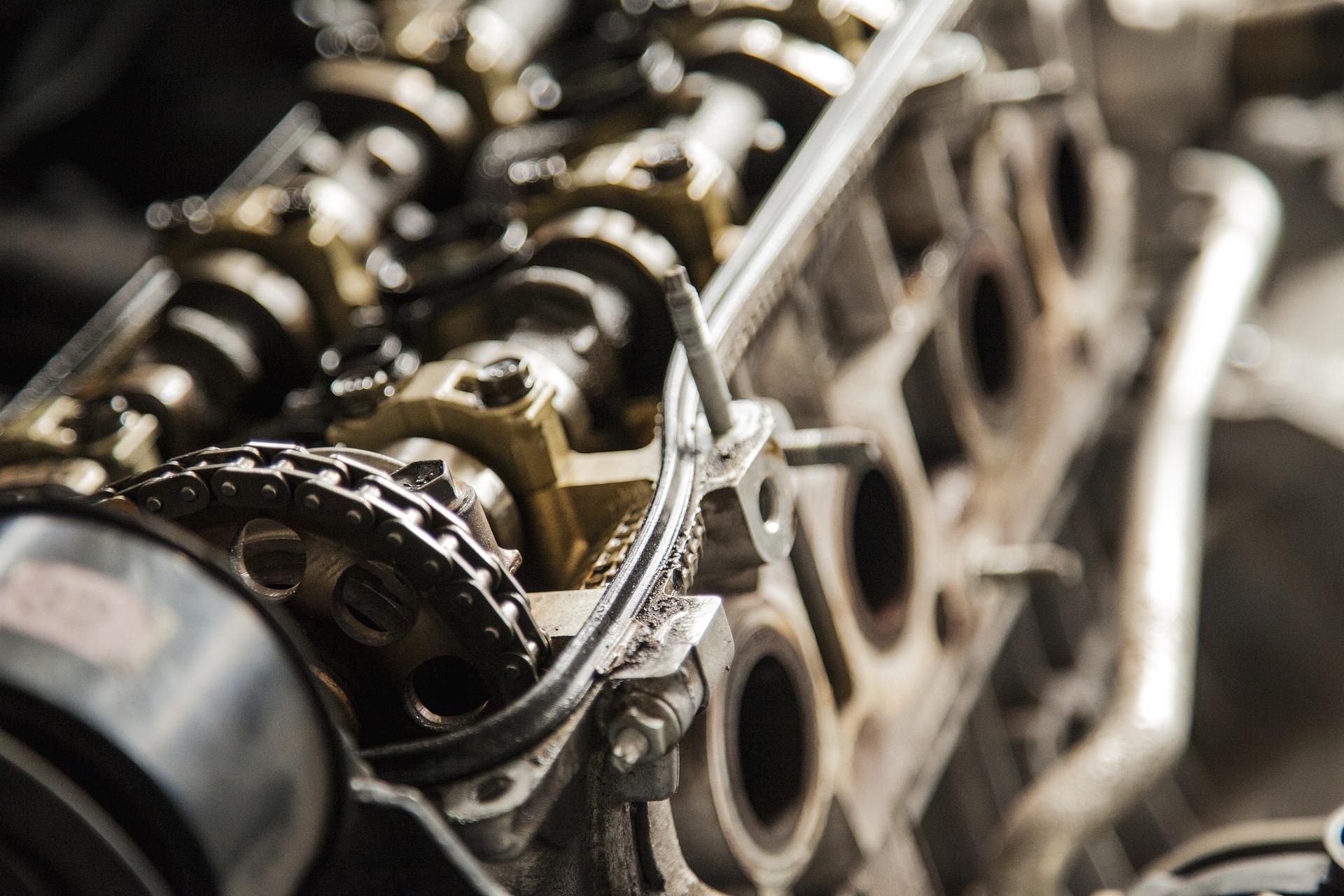
Ship Engine Basic Configuration
Ship Engine Basic Configuration
2019/04/10 - [자동차 & 선박 디젤 엔진 ] - INSTRUCTION MANUAL HEAVY DIESEL ENGINES!! INSTRUCTION MANUAL HEAVY DIESEL ENGINES!! Information sharing on diesel engines I am a Korean. Please understand even if I am not good at English. As I am interested in korea ship engines and korea car engines, I would like to share the inf.. ezexec2.tistory.com Ship Engine Basic Configuration The Diesel is designed as a ..
 거버너(GOVERNOR)의 구조 및 기능
거버너(GOVERNOR)의 구조 및 기능
거버너(GOVERNOR)의 구조 및 기능 디젤 엔진에서는 최고 회전을 제어하고 엔진에 무리가 가는 것을 방지함과 동시에 저속 시의 회전을 안정시키기 위하여 거버너를 사용하고 있습니다. 특히 저속 회전 시의 연료 분사량은 매우 적은 양이기 때문에 제어 래크의 약간의 움직임에 대해서도 분사량의 변화가 커지므로 회전수가 크게 변하게 됩니다. 또한 엔진의 부하 변동에 의해서도 거버너가 없으면, 그것에 추종할 수 없기 때문에 시동이 꺼지기 쉽고 원활한 운전을 할 수 없습니다. 그 때문에 엔진의 회전수나 부하가 변화한 경우, 자동적으로 제어 래크를 움직여서 분사량을 제어하며, 회전을 안정시키는 거버너가 필요로 하게 됩니다. 거버너는 회전수와 부하에 따라 변동하는 흡기 매니폴드 내의 부압을 이용하는 공기식 거버 나와..
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- 로또박사
- 조선
- 조선단어
- 조선용어
- 디젤엔진
- 로또1등당첨지역
- 로또당첨번호
- 흡기
- bmw리콜
- 인물꿈
- 선박
- 거버너
- 해양조선
- 해양플랜트
- 꿈풀이
- 꿈해몽
- 해양언어
- 해양용어
- 선박용어
- 선박단어
- 배기
- 의장
- 엔진 정비
- 오늘운세
- 흡배기
- 해양단어
- 선박부품
- 속도조절
- 연금복권 당첨번호
- 조선말
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |